Routers and access points with Wi-Fi have been an essential attribute of home and mobile Internet users for 10 years now. One day, the speed of the Wi-Fi network can be greatly reduced, and sometimes the wireless connection disappears completely and for a long time.
The main reasons for disruption of the Wi-Fi network
Problems with wireless Internet access can be due to various reasons: router failures, incorrect computer or smartphone settings, interference from nearby equipment, etc. Viruses and even the actions of hackers can disrupt the operation. In all cases, you need to identify the cause of the malfunction and try to eliminate it - first yourself, and if that doesn’t work, then turn to professional computer specialists.
The Wi-Fi network is visible to devices, but they do not connect to it
There may be several reasons why there may be no connection to a Wi-Fi network.
Wi-Fi network is not visible to devices
There are several reasons why the Wi-Fi network is not visible from a gadget or PC.

Wi-Fi on PC or tablet does not work after reinstalling Windows
There are several reasons - from hardware to software.

Video: WI-Fi does not work after Windows 10 update
Laptop or tablet is connected to Wi-Fi, but there is no Internet
The reasons are due to the fact that the router does not have Internet access.

There is Internet via Wi-Fi, but it turns off on its own
There may also be several reasons.
- Inadequate Internet connection quality. If the provider has an unreliable communication channel or, in the battle for first place in the list of the most popular operators, has gone too far with the number of clients, the speed of individual users will be very low, the connection will often reconnect due to equipment overload, and incoming traffic will freeze. Previously, cellular providers suffered from this - at the initial stages of development of the 2G/3G/4G coverage area, demand, in the context of a collapse in the price of 1 MB of traffic, was far ahead of the construction and launch of new network facilities.
- The router's RAM freezes (data buffer overload). Restarting it will help.
- The device has overheated - any modern technology has protection against overheating of microcircuits. Both the CPU/RAM of the router or access point, as well as any of its microcontrollers that process data incoming/outgoing via LAN or Wi-Fi, can overheat. It is advisable to turn off the router for at least a few minutes.
If the 3G/4G signal is poor and the Internet speed is high, the 4G modem used with the router may also overheat. Users of Android smartphones and tablets (Yota subscribers), who distributed up to 40 GB every day via Wi-Fi (in the 2000s, these were Nokia and Motorola mobile phones connected via cable or Bluetooth), talk about cases when the device got hot like a kettle and turned off every hour or two of downloading/distributing torrents on the PC. The same thing happens with routers.
Wi-Fi does not work due to firmware glitches and viruses
No matter how simple, friendly and secure the firmware (firmware) of the router is, the router itself is not protected from malfunctions and viruses. Virus technologies disrupted the operation of Apple, Android and Symbian gadgets. The virus code penetrated card machines, ATMs and access control systems at protected sites with the Internet, and disabled the firmware in USB modems. Routers are also not insured - neither purely wireless from Beeline or Yota, nor home ZyXEL and TP-Link, nor Cisco access points, nor purely cable equipment used in facilities where any wireless element is prohibited by security rules.
Software failures can occur either due to inept flashing (through ignorance or accident, the power is reset during a firmware update in the router’s flash memory), or wear and tear of the flash memory chip itself (it’s impossible to even enter the router settings - underloading of the web pages interface in the browser).
Virus activity is expressed in reprogramming the router settings: changing the IP DNS to the values of the malicious server, substituting primitive passwords or turning off Wi-Fi security settings, switching wired protocols and cellular network operating modes, etc. To fix this, do the following.

Sometimes the virus changes the firmware file just before it is downloaded to the router. The solution is to remove viruses from the PC, using all means including formatting the drive (of course, transferring valuable data to other media before doing this) and downloading the official firmware version again from the manufacturer’s website.
Slow Internet speed via Wi-Fi
The reasons are related to both the quality of network access and Wi-Fi communication parameters.
- Low speed cable or cellular provider tariff. If the Rostelecom company and its dealers have unlimited speed, then in cellular networks, for example, in MegaFon or MTS, after a certain number of gigabytes of traffic per month, the speed drops to 64 (or 128) kbit/s. Change tariff and provider.
MTS limits the connection speed on the “Hype” tariff after the subscriber uses up 7 GB of mobile traffic per month
- Unstable operation of LAN-Ethernet 10/100 networks. You can feel how the speed has dropped sharply due to a damaged provider cable coming from the optical terminal at the entrance to your apartment by watching movies in (Ultra)HD format online: movie playback, which was still stable yesterday, “slows down” every second , loading data. A few years ago, the provider himself was to blame, but now the speed of the same Rostelecom subscribers has increased so much that 95% of the time it will be normal, excluding evening hours, when the load is maximum. If online video constantly slows down, you can with 100% certainty suspect a fault with either the cable or the router itself.
If the cable or router malfunctions, the connection speed drops sharply
- Router data buffer overload. Restart it.
- You are too far away from the device. In fact, the Wi-Fi speed, depending on the distance between the router and the gadget/PC, as well as the level of the Wi-Fi signal on the gadget itself, fluctuates hundreds of times - from 1 to 300 Mbit/s, this is how Wi-Fi technology works. If in one room the speed is 150–300 Mbit/s, then in the next room it can already be from 11 to 54 Mbit/s, and in the entrance or on the street it can drop to 1 Mbit/s. Wi-Fi interruptions will not affect your cable connection (LAN cable length up to 250 m).
Choose auto speed switching using Wi-Fi technology
The last point requires clarification. The fact is that the Wi-Fi speed is switched by the router and the gadget automatically. Even if you forcefully turn on the maximum (802.11n or 150 Mbit/s), then if you go into the next room, you may lose your connection to the Internet - incoming and outgoing traffic will freeze, websites will stop opening and messengers will stop working, even simple ones like ICQ , since the lower level speed (802.11g, or 54 Mbit/s) will not be enabled.
Different types of Wi-Fi networks support different data transfer rates
Check the auto speed selection in the router settings.
Advice for experimenters: without highly directional antennas and amplifiers, do not be located far from the router.
Video: how the provider’s speed is “cut” by the router via Wi-Fi
Other Wi-Fi errors and their solutions
The full list of errors in Wi-Fi operation is not limited to failures of the Wi-Fi repeater alone or problems on the provider’s side.
Network cable is not connected
The provider's network cable connected to the WAN socket may not be connected either to the router itself or to the entrance terminal. The reasons are as follows:
- damaged cable wires;
- broken RJ-45 connector retainer holding the cable in the LAN socket;
- power outage (the terminal has no autonomous power supply);
- malfunction of the LAN interface in the terminal and/or router (burnout of network equipment throughout the entire area from electrical interference, an accidentally dropped network wire, static discharge when touching materials or a lightning strike on external cables);
- a faulty LAN network card in a PC or laptop (it happens that the adapter in Windows is detected as a working device, but the connection cannot be recognized);
- viruses on PCs that overload Windows performance (displaying incorrect connection status or connecting with a delay of minutes or hours).
The connection is already in use or not configured
Error 651 indicates that the modem or dedicated one is already in use or has not been configured.
If the router is not configured or is already in use by other processes, error 651 is displayed
Your connection needs to be removed and reconfigured. The instructions are suitable for Windows 7/8/10 - working with the network connection setup wizard in the latest versions has not been enriched with anything special.
- Give the command “Start - Control Panel - Network and Sharing Center”.
Network Preferences Center is ready to go (Windows 7/8/10)
- Select to create a new network connection.
To create a new connection, select the network connection option
- Select to create a high-speed connection.
At the step of selecting the connection type, set to work using the PPPoE protocol
- Enter the connection name, login, password, and check remember password. It is advisable to enable the use of this connection by other users (if the problem is common to everyone).
After clicking the “Connect” button, a connection to the Internet will be established. If the problem persists, contact your provider's support. In the worst case scenario, reinstalling Windows helps.
Infinitely obtaining an IP address from the router
Without receiving at least a temporary IP address from the DHCP IP address numbering range of the router, the gadget or PC will not be able to access the network. And this is typical not only for Wi-Fi connections - the assignment of an IP to a computer or mobile device was established when TCP/IP was created.
If the device freezes at the stage of obtaining an IP address, you need to check the router settings
You need to check the router's IP settings.
Checking Wi-Fi settings
Do the following.
- Restart your router.
To avoid unplugging the power adapter, press the power button twice
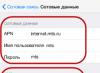
- Give the command “DHCP - DHCP settings”, check whether the DHCP function is enabled and what address range is assigned to third-party devices.
Make sure WPA2/TKIP encryption is enabled and a key you know is assigned
- Go to the “MAC address filtering” item and check that the MAC address filter settings are disabled and the option “Accept requests from devices whose MAC addresses are not listed” (Allow the stations specified by any enabled entries in he list to access) - installed.
MAC address filtering often causes confusion when Wi-Fi security requirements are less stringent
- Save your settings by clicking the “Save” button on each page and try reconnecting.
You may need to restart the router again.
Checking services and connections in Windows
Ensure that all services, addresses, and protocols critical to the network are enabled correctly. The following services are responsible for Windows networking capabilities:
- DHCP client;
- DNS client;
- WLAN auto-configuration service;
- web client;
- IP auxiliary service;
- routing and remote access;
- server.
Do the following.

The connection of the router or cable modem to the network is broken
ADSL modems, popular in the 2000s, are being actively replaced by ONT modems (optical network terminal) - these devices support Internet speeds of up to 1 Gbit/s (using GPON technology), which differs from the throughput of an ADSL modem by 10 times. Already, Rostelecom and local providers provide Internet speeds of about 35–100 Mbit/s.
The reason for the decrease in Wi-Fi speed may be not only the reduced external speed at the cheapest available tariff, but also damage to the optical cables in the section ONT-modem - home rack-terminal - the nearest provider node. The LAN cable between the router and ONT modem may also be damaged.
The router in access point mode acts as a LAN/Wi-Fi distributor
The user can diagnose the entire subnet of the router (the router itself and its external cable). In case of damage to cables and equipment, including the ONT modem, telephone, IPTV set-top box and cables in the entrance, you should use the help of technical specialists from the same Rostelecom. This is also explained by the fact that if a twisted pair cable can be restored/replaced independently, then the subscriber simply may not have the tools to splice damaged fiber-optic lines.
Video: Tablet does not connect to Wi-Fi - overview lecture
Solving problems with Wi-Fi at home and at work is not particularly difficult. In many cases, the user will figure it out on his own. The help of a specialist is required only in cases where problems arise on the provider’s side.
A Wi-Fi router is a useful device that relieves the user of the need to be literally tied to the Internet by wire. According to numerous experiments, the signal range of an average power router reaches 100 meters indoors, and 300 meters outdoors. Once configured, a wireless router does not require any additional maintenance, it is extremely easy to use, but, like any technical device, it is not immune to failures and breakdowns.
Examples when a seemingly correctly configured router does not distribute Wi-Fi are not that uncommon. In this case, the network status, depending on the nature of the problem, can be “No Internet access” or “Restricted”, although a scenario in which the network is detected by the system, but there is no actual connection or large traffic losses are observed, is also possible. In this article we will try to figure out why the router does not distribute the Internet via Wi-Fi, and at the same time we will see what can be done in this or that case.
Temporary failure of the router
If the router works day and night, its operation may sooner or later fail, so the very first thing to do if the router stops distributing the Internet is to turn it off, wait a few minutes, and then turn it on again.
Rebooting the router can also help the device (computer or tablet) detect the network if it is suddenly not detected when the device is turned on. Users of devices connected to one or another wireless network often encounter this problem.
Problems on the provider side
If rebooting doesn't help, the next thing to check is whether there are any restrictions from your internet service provider. It is likely that there was an accident somewhere on the server, the backbone cable was damaged, unplanned maintenance work is being carried out, and you will delve into the settings and be at a loss as to why the router does not distribute Wi-Fi. Call your provider's technical service number and make sure that the problem is not on their side, and only then look for the source of the problem on your own.
Hardware faults
At the next stage, we check the serviceability of the equipment - cables and router. If the power light does not light, the power cord or power supply may be damaged. We check the condition of the cables in the house (apartment) and outside it, and see if the plugs fit tightly in the sockets. Many modern routers have hardware power on/off and Wi-Fi distribution buttons.


It often happens that someone at home picked up the router and accidentally pressed one of these buttons. This point also needs to be checked. The wireless network indicator deserves special attention. If the Wi-Fi icon on your router is not lit, this could indicate several problems.
- Breakdown in the distribution system. You can’t do anything here yourself, you need to call a specialist.
- There is a problem with the router software. It can be eliminated by rebooting, adjusting or resetting the settings, or, in extreme cases, flashing the firmware.
- The Wi-Fi sharing button is disabled. In this case, the router does not distribute Wi-Fi, but the Internet is available and you can connect to it through the router via cable. If a cable connection is only possible directly, without a router, this may indicate either a breakdown of the device or a failure in its settings.
Incorrect Wi-Fi settings
Incorrect router settings are most often indicated by a lit but not blinking Wi-Fi indicator, as well as a change in its color from green to orange or red. The problem is resolved by correctly configuring the network settings. This procedure is somewhat different in different router models, although the principles are the same. If you have never configured routers before, it is best to entrust this task to a specialist called to your home; at a minimum, you can check whether the wireless network is enabled in the device settings.
To enter the router settings, connect it to your PC via cable, go to 192.168.1.0 or 192.168.1.1 in any browser and log in with your login/password (admin/admin by default). In TP-Link routers, for example, you need to go to the “Wireless” section and check whether the “Enable Wireless Router Radio” item is checked. The checkbox “Enable SSID broadcasting” must also be checked, otherwise devices will not be able to see the network. In other models, the setting may be located in a different place (look for the Wireless network or WLAN section).

A very interesting case is when a laptop sees the network, but a smartphone or tablet does not. It turns out that the router does not distribute the Internet via Wi-Fi only to mobile devices. Owners of smartphones and tablets brought from the United States sometimes have to face this problem. The reason for this is the discrepancy between the channel selected in the router settings and the settings specified in the firmware of the mobile device. The problem is usually solved by manually selecting the channel, 1st or 6th.
Incorrect network adapter settings
If Wi-Fi does not work on the router, this does not always mean that the problem is hidden in the router. It is quite possible that the settings on the receiving device - a computer, laptop or tablet - have gone wrong; in any case, it won’t hurt to check the configuration of the wireless adapter. Open with command ncpa.cpl network connections, go to the properties of your wireless network, in the list of parameters on the “Network” tab, find the item IP version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and double-click on it.

In the properties window that opens, set to obtain the IP address and DNS server address in automatic mode. If automation is already set, try manually setting the DNS address 8.8.8.8 (Google) or 77.88.8.88 (Yandex). You can also set the address of any other alternative DNS server, which is not difficult to find on the Internet.


Conclusion
Hello friends! Wi-Fi Internet is no surprise to anyone now; it is available in almost every office, store, cafe and is actively appearing in homes. A large selection of routers and their low price only contribute to such an active installation of wireless access points. Almost everyone can afford to buy a router and install it at home, because it is very convenient and not expensive.
And if routers have become very popular, then the question of setting up, connecting, breaking, etc. of these same routers has become relevant. If I have already written a lot of articles on connection, settings and various errors, which you can read in the “ “ category, today I want to talk about the most popular failures of Wi-Fi routers and give some tips that will help you fix the device, or simply determine reason.
There are a lot of comments left on this site about various problems with routers. And very often the cause of some error is not the settings (as many people think), namely technical problems in the router itself (in the hardware).
Today I want to talk about problems that appear unexpectedly. Like this? Well, the router worked great, distributed Wi-Fi, made everyone happy :), and then it stopped working. It doesn’t matter how it stopped working completely, or simply not how it should work. The main thing is that it used to work well and stopped working on its own (You haven't changed any settings).
It’s just that the problems that appear during the first setup of the router most likely arise due to incorrect settings.
The router does not respond to connection to the power grid
I'm sorry, but your router is most likely completely dead. On every router (well, or almost every one) There are performance indicators.
And if these indenters do not light up when you connect the device to a socket, then this is very bad.
What can be done?
Well, first check if there is a power off button on the router. There is such a button on the TP-LINK TL-MR3220:
If the button is on, then you need to check the power supply, it may be the problem. Typically, power supplies burn out more often than the routers themselves. Perhaps your neighbors have the same router, run and ask for a couple of minutes.
If the device still does not work, return it under warranty. And if there is no warranty, then it is better to throw it away and buy a new one than to send it for paid repairs. Although, you can take it to a workshop, perhaps the repair will not cost very much.
Why does this happen?
For many reasons. There may be a manufacturing defect, but most likely the router burned out due to unstable voltage in the network, a thunderstorm, or moisture. If possible, connect the router through a voltage stabilizer. Well, or just turn it off when you see that there is going to be a thunderstorm.
This was the most severe case, now let's look at milder breakdowns.
The router has stopped working and does not provide internet access
If a problem suddenly arises with Wi-Fi, for example, all devices stop connecting to the router, there is a connection, but the Internet does not work, etc. then do not rush to throw your router out the window :).
First you need to find out that the problem is really with the router, and not with the device you are trying to connect. How? Just try connecting another device (laptop, tablet, phone). If only one device does not connect, then the problem is most likely in it. Well, you understand what I mean.
The problem is in the router, what needs to be checked and how to solve the problem?
- Don’t rush to immediately go into the router settings and change something there right away. Otherwise you set it up in such a way that it definitely won’t work. Believe me, I’m not just writing this :).
- Reboot your router. Restart your computer (phone, tablet).
- Call your provider and ask if there are any problems on their end. Explain your problem to them. Perhaps the Internet is not working due to problems with the provider’s equipment.
- Check whether your Internet is paid for and whether it is active (You can also ask your provider for this).
- Check all connections. Internet cable that connects to the router. It is advisable to check this cable outside the apartment (house). Perhaps your cable was simply cut. On purpose or by accident - this happens.
- Look at the router case, maybe there are some interesting buttons that someone accidentally switched. For example, there may be a button to disable the Wi-Fi module. If you click it, devices will not see your wireless network.
- Go to the router settings and see if the settings have been lost. This may happen and the Internet will not work. Especially, check the WAN tab, where the settings from the provider are. If they fail, set them up again. Here is an article for you as an example
- Try changing the channel in the router settings. Here is a detailed article. How might this affect strange Wi-Fi problems? Perhaps your neighbors have installed a router and more than one, I will introduce neighbors above, below, on the sides. And just all the channels (or the one you are on) busy. That's when problems begin that are even difficult to explain.
Have you tried everything and nothing helps?
Then, I advise you to send the router for repair, again under warranty. And if there is no warranty, then pay for repairs, or buy a new one. Before doing this, you can ask a friend who understands this matter (if there is one) so that he can look at the router, settings and connection.
Real case. My TP-LINK TL-MR3220 router worked great for several months. Then, suddenly it stopped detecting the 3G modem connection. I connected different modems, the modem gets power, but it does not appear in the control panel. I tried everything, even the special firmware that TP-LINK support sent me - it didn’t help. You can read more in the article.
What I mean is that if a technical problem occurs in the router (something will burn out there), this does not mean that it simply will not turn on. It may work, but it won't work as intended. And it can take a very long and painful time to configure, flash, check, etc.
Don't suffer. You paid money for this device. Call support from the router manufacturer and explain the problem to them. I'm sure no one will give you better advice than them.
If support cannot help over the phone, they will advise you to apply for warranty coverage (if there is one). And then it’s up to you to decide whether to go for repairs or buy a new device.
We all use the Internet while in cafes or restaurants, with friends, even at home at the dinner table, checking mail or messages on VKontakte. As practice shows, one of the most common problems occurs when working with Wi-Fi wireless technology. Let's say our access point is located in the house from the router or in a public institution. Everything seems to be configured correctly, but for some reason there is no access to the network.
So, what to do if you encounter such a problem? In fact, there may be a dozen reasons, each of which we will consider in this material!
Wi-Fi on Android is turned on, the status is “Connected”, but there is no Internet access
Let's say that you have activated Wi-Fi on your smartphone and connected to an access point. Your phone displays the “Connected” status, but you cannot access the Internet, either using a browser or through other programs, for example, Odnoklassniki. What should we do in this case?
First you need to check whether the Internet works for this connection at all. That is, you need to gradually filter out the list of possible causes using the method of elimination, and checking the Internet is the very first of them.
Try connecting to this access point from another device and go online. If everything is fine, then the problem is in your smartphone. If another device does not connect to the Internet or does not open websites, then the problem is with the access point or router itself.
Solution 1 – Correctly setting up your router for Wi-Fi
First, check if your smartphone is within range of a wireless network. Typically, routers can distribute a signal up to 200 meters, provided that there are no obstacles within this radius. If everything is in order with this, then move on to the router settings.
Change the channel your access point is on. Usually it is set to Auto, but we advise you to set it to channel 6 or another. Select any of the available ones, save the changes and check the functionality.
You can also change the operating mode for Wi-Fi. As practice shows, by default the 11bg mixed mode is usually set everywhere. Change it to 11n only.
If you have a column in the settings for specifying the region, then be sure to set your region there. This is a minor parameter, but in very rare cases even it can affect the correct operation of the access point.
Solution 2 – Setting up a proxy server
Another possible problem is the automatic selection and installation of a proxy server for a specific access point on a wireless network.
To fix this:
- Go to Settings on your device
- Next, select Wi-Fi or “Wireless Networks”, depending on the version of Android
- Find the access point you are connected to and hold your finger on it for a few seconds. An additional menu will appear in which you need to click “Change network”
- Check the box next to "Advanced options" and select "Proxy settings"
- All that remains is to check the box next to “No”, after which the proxy server will be deactivated
Wi-Fi is enabled on Android, but Google Play and other apps are not working
If Wi-Fi is activated on your smartphone and it is connected to a certain access point, but the phone does not open websites or load pages and applications on Google Play, check that the time and date settings are correct. This is a very common user mistake! In 90% of cases, it is this that causes connection problems.
You just need to set the time and date correctly, reconnect the Internet, then try to log into Google Play and view one of the applications on the page.
Why Wi-Fi doesn't work on Android: other reasons
- Incorrect password. Sometimes the Android operating system stores the password for a certain access point, but when you subsequently connect to it, no notification appears that the password is incorrect. We advise you to check the correctness of your entry and change it if necessary. As you understand, public places usually have open access points, but there are also closed ones. To select a password for them, you can use special programs, for example, from the same Google Play, where users share information around the world.
- Software problems. Another common reason that is related to your system software. To check if it's working correctly, you can use the Wi-Fi Fixer app. Just install it on your device and run it. There you will also be able to view a complete list of networks for which the data you have previously connected to has been saved. Restart your phone and try connecting to the hotspot again.
- Malicious applications. There may be viruses or Trojans on your phone that are blocking wireless networks. In this case, you will have to manually install an antivirus, for example, Kaspersky.
- Incorrect settings. We have already talked about setting up Wi-Fi networks. If you can’t change them, you can simply reset to factory settings. You may also have old entries about the access point. For example, you connected to it, as it says in the system, although the connection was not actually made. Just update the list of networks in the settings or delete everything and try updating again, and only then connect to a specific Wi-Fi point.
But what should you do if Wi-Fi is connected, but the Internet still does not work even after all the recommendations described? Most likely, your Wi-Fi module itself is not working correctly. The following will help:
- Phone firmware, if the reason lies in the software part of the smartphone. If you do not know how to flash Android operating systems yourself, it would be better to contact a service center.
- Repairing the Wi-Fi module. If the phone's firmware does not help, then the problem lies in the wireless network module itself. In this case, you will have to take the smartphone to a service center and have the parts replaced.
This is not a complete list of reasons that cause Wi-Fi malfunctions. If you have encountered similar situations and you solved them in some other way, be sure to tell us about it in the comments for our readers!
All of the above reasons and their elimination should lead to the network connecting, otherwise the router is simply faulty and needs to be replaced.
Magic WiFi programs. The latest development of computer technology specialists is the Magic WiFi program. This program allows a network card to become an access point. Installing the program on a laptop or other electronic device automatically turns it into a kind of router that distributes Wi-Fi.
What to do if the magic wifi wireless network adapter is not found? The adapter serves to strengthen the Wi-Fi transmission signal and, if the device does not see it, you need to remove the adapter, then update the configuration and list of networks, and restart. If this does not help, then set all network parameters manually.
Why don't other devices work? When Wi-Fi is connected, neither the tablet nor the phone is online and does not receive a signal.
Devices do not see Wi-Fi signal
Here you can point out several factors, when corrected, as a rule, everything returns to normal. Having eliminated these reasons, we will restore connections with other devices via Wi-Fi.
Four reasons for no signal:
- there is simply no receiver for Wi-Fi;
- the password is entered incorrectly;
- The router or modem has a limited number of distributions (say, up to 4);
- You need to change the router settings.
Why is the Internet connected only via Wi-Fi? You immediately need to check everything that is connected to the Internet via Wi-Fi. It turns out that on some devices everything is normal, but on others it is not, which means the reason is in the device settings.
Perhaps the whole problem is in the router, then you need to reset its settings and configure it again. The setup is carried out according to the instructions issued by the provider.
Reset settings with button. Also, a quick reboot of the device can solve the problem. To reset the settings, you need to find the “reset” button and hold it for a few seconds. There is an alternative option - this is the WPS button.